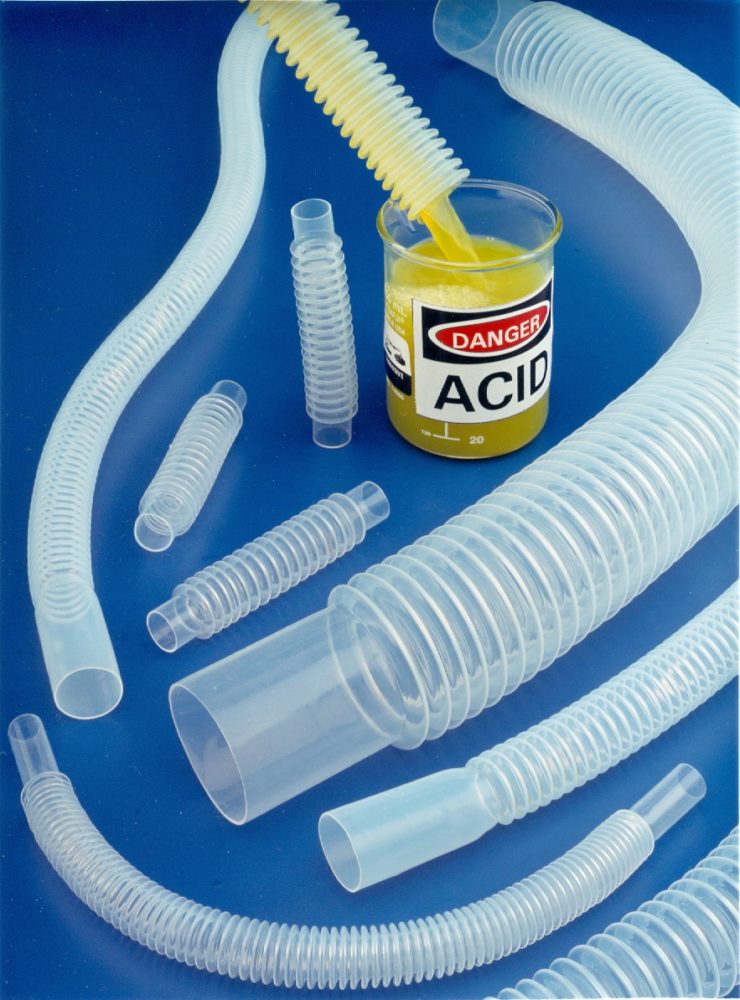
The commercial production and use of plastic corrugated tubing in the United States began in 1967, following the invention of corrugation extruding machines in the early 1960s in Germany and designs made by Ira Clement in 1966 for Penn Tube Plastics in Pennsylvania. Initially made from polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride or polypropylene, corrugated tubing made from plastics offered a means for transporting liquids that were crush resistant and could turn sharp corners, while also capable of offering very small bend diameters without decreasing the piping’s inner diameter. Corrugated tubing was initially used to fill bottles on assembly lines, and later for paint solvents due to these polymers’ high resistance to chemicals. Its use in subsurface drainage grew as well, largely replacing concrete or clay piping due to plastic corrugated tubing’s flexibility and chemical resistance, along with the fact that its much lighter weight made it easier and quicker to install, reducing labor costs. Corrugated tubing made out of plastics is now used in many fluid handling applications, though it has since developed many other uses, including as a conduit for electrical wiring or for transporting gases.
Types of Corrugated Tubing
Though there are many types, two of the most commonly used are FEP (fluorinated ethylene-propylene) and PFA (perfluoroalkoxy) corrugated tubing. Both are fluoropolymers and are used in multiple industrial applications.
Benefits of FEP Corrugated Tubing
FEP corrugated tubing has a number of benefits that make it particularly useful. These include:
- Ability to turn sharp corners without reducing inner tubing diameter.
- Can be braided with stainless steel for use in higher pressure applications.
- Low refractivity allows operators to monitor material passing through the tubing.
- Non-stick surface allows for easy cleaning.
- Offers excellent electrical insulation properties.
- Operates well in high temperatures; maximum continuous operating temperature is 200° F (93° C).
- Resists most strong corrosive liquids, including hot acids.
Benefits of PFA Corrugated Tubing
PFA corrugated tubing combines the benefits of FEP and PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) It’s also known by its brand name, Teflon, which is used for fabricating non-stick cookware. It offers better heat resistance, along with an ability to resist chemicals, so is considered a more robust material for corrugated tubing. Though a more expensive option, its advantages make PFA worth the cost. Its benefits include:
- Acts as an effective substitution for stainless steel tubing.
- Can be used with both fluids and gases.
- Completely clear plastic that is UV-transparent, so allows for operators to monitor whatever passes through the tubing.
- Does not degrade quickly over time, so material lasts longer.
- Flame resistant.
- Its non-stick properties allow for easy conveyancing.
- Offers exceptional resistance to chemicals.
- Operates well in higher temperatures; maximum continuous operating temperature is 300° F (148° C).
- Provides the lowest permeability of any fluoropolymer.
- Uses no silicone.
- Works across a broad range of temperatures, from extreme heat to extreme cold.
Applications for Corrugated Tubing
Both FEP and PFA corrugated tubing have many important applications through a wide range of industries.
FEP Corrugated Tubing Applications
Typical applications for FEP corrugated tubing include:
- Aerospace industry – relies on engineered FEP corrugated tubing to withstand wide variations in temperatures and to prevent damage from highly corrosive chemical fuel.
- Food & beverage industry – provides a nonstick and sterile surface along its internal length as well as a low temperature shrink rate.
- Water treatment industry – used for purifying water. Its high melt temperature allows it to be used in heat sterilization, as it can withstand hot water without damaging the tubing. As an excellent UV transmitter, FEP tubing also works well with UV water treatment processes.
- Biopharmaceutical industry – used for laboratories, diagnostic equipment, cell transport and sterile filling, as FEP is highly resistant to chemicals, does not absorb materials and its easy-to-sterilize surfaces make it exceptionally useful in biological and pharmaceutical laboratories.
- Environmental industry – due to its non-leaching properties, it is used in higher quality equipment for testing water, soil and air to ensure samples are not contaminated.
- Electrical industry – due to its high electrical breakdown voltage and low dielectric constant, it makes a good choice for insulating coaxial cables and computer wiring. As FEP tubing also has a smaller diameter, it saves space when used for such applications.
Many other sectors use FEP tubing, including automotive, medicine, scientific research and heavy industry. In fact, it often offers a more economical choice for various industrial applications that use PFTE tubing.
PFA Corrugated Tubing Applications
When it comes to PFA corrugated tubing, its applications include:
- Biotechnology industry – used for multiple purposes within this sector, including fermentation labs used for research and development. PFA tubing transports materials between fermentation tanks and storage units, with its clear exterior allowing accurate monitoring of material flow, clogging and material deposits within the tubing to enable quick remediation.
- Food & beverage industry – helps transport foods and beverages as it remains sterile, prevents particles from accumulating and retains integrity up to 500° F (260° C). PFA tubing is often used rather than stainless steel for filling water bottles.
- Pharmaceutical industry – due to its ability to preserve material purity, along with its resistance to chemicals, acids and other corrosive materials, PFA tubing offers an excellent choice for a sector that relies on keeping contaminants out of its products.
- Semiconductor and microprocessor industry – used for the same reasons that research labs and pharmaceutical companies use it, PFA tubing preserves fluid purity. As PFA tubing also has a high resistance to chemicals, it’s extremely useful for keeping contaminants to a minimum while ensuring semiconductors and microprocessors are kept immaculate.
As per FEP corrugated tubing, PFA tubing has many other uses and applications within other sectors and can be used in place of FEP tubing when a more robust solution is required. Due to its optical transparency, flexibility and high chemical resistance, PFA is more expensive than many other polymers, though it is often used in combination with carbon steel fibers as a replacement for more expensive metals or alloys.