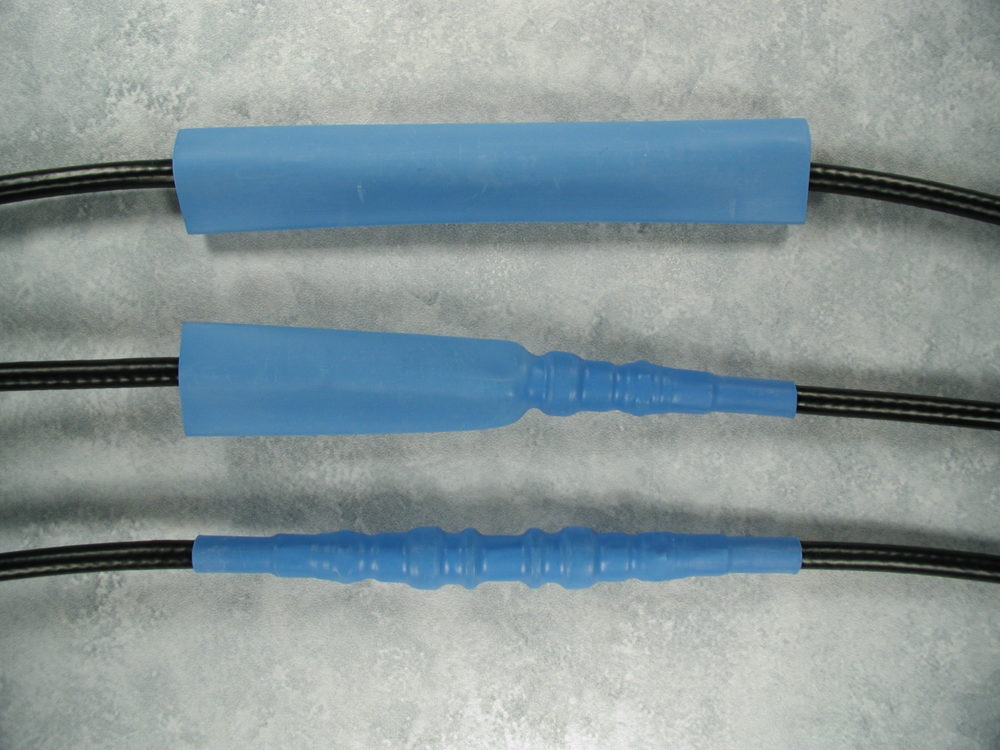
Commonly used in electrical setups, heat shrink tubing insulates electrical components from harmful elements in their immediate surroundings. This includes protecting against abrasion, dust, moisture and other environmental factors that can damage wiring or cabling. It’s sometimes referred to as electrical shrink tubing due to its most common use, protecting and organizing electrical arrays. Certain heat shrink tubing materials work better when used for specific applications, so understanding the differences between them will help when choosing the best for a particular purpose.
What is Heat Shrink Tubing
Made from thermoplastic tubing, when exposed to higher temperatures heat shrink tubing does what its name says. It shrinks. Used to protect electrical components and wire arrays, the tubing reduces in diameter to snugly fit around contours as a protective extra layer. Heat shrink tubing covers both individual and bundles of wires or cables.
Applications for heat shrink tubing include:
- Bundling wires or cabling following the same pathway.
- Creating a more aesthetically pleasing appearance.
- Identifying for coding purposes when colored tubing is used.
- Insulating electrical wiring from electricity and heat.
- Protecting against abrasion, chemicals, dust and water.
- Reinforcing cabling to relieve strain when held under tension.
- Repairing damaged or exposed wires.
Its uses are also often dependent on the heat shrink tubing material used. Industrial uses include their use in protecting cable harness assemblies, where they envelop implements to act as insulation, labeling, mechanical protection and for aesthetic purposes. In households, heat shrink tubing is used primarily to insulate cables or wires while also protecting against abrasion and chemicals.
Best Types of Heat Shrink Tubing Material
The best heat shrink tubing material depends on the specific application for which it’s used. Some materials work better for specific purposes, while others serve more general uses.
Heat shrink tubing materials used to protect wiring, cabling and tubing include:
- Elastomer (PES): used widely in industrial environments for protecting cabling due to its flexibility and resistance to abrasion and caustic fluids.
- Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP): resists chemicals and often used as sealant.
- Polyolefin (POX): a synthetic polymer most widely used due its resistance to both chemicals and high temperatures.
- Polytetrafluorethylene (PTFE): synthetic compound highly resistant to both chemicals and friction.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): used widely for heat shrink tubing material because of its smooth surfaces and versatility.
- Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF): extremely robust and highly resistant to chemicals, flame and industrial fuels.
- Silicone: used in medical environments due to its ability to withstand sterilization, it’s flexible and resilient to extreme temperatures.
Along with its ability to shrink when heated, this tubing consists of two basic types. These types are known as single (or thin wall) and dual (or double-wall) tubing. Single wall tubing is robust and reliable, making it a good choice when protecting against abrasion and strain, along with insulating from electricity. Double-wall tubing offers a firm seal and protection from corrosion, with its added adhesive layer providing protection from wetness.
PVC Heat Shrink Tubing
A highly flexible heat shrink tubing material, PVC forms a smooth, tight-fitting layer and acts as insulation for most functions. It offers resistance to sunlight, moisture and fungus, along with most oils and chemicals. With its low shrink temperature below 200°F (about 93°C), PVC heat shrink tubing provides both mechanical and electrical protection against damage to both cabling and components enclosed in it. It conforms well to sharp bends without rippling, making it useful for protecting against busbars, appliance handles or other elements that can potentially damage cabling or wiring.
Polyolefin Heat Shrink Tubing
Flexible polyolefin is a material used for heat shrink tubing that provides exceptional flame resistance, while additionally balancing various chemical, electrical and physical properties. Rated for continuous operation in temperatures from -67 °F (-55°C) to 275°F (135°C), it can additionally withstand temperatures reaching 572°F (300°C) for short durations. This heat shrink tubing material works well as a fire-resistant covering, for packaging components and as a less-weighty option for wrapping wire harnesses.
Heat Shrink Tubing by M.M. Newman Corporation
M.M. Newman Corporation supplies two types of heat shrink tubing. Materials the company offers – PVC and Polyolefin – work well for a variety of industrial and military applications. The company takes great pride in its ISO 9001:2015 certification, which indicates to our customers the high-quality service and products we provide. Along with heat shrink tubing to protect cabling and wiring, we specialize in Heli-Tube® spiral wrap, hot tools, soldering irons, and PTFE tubing. For more information, contact M.M. Newman Corporation today.